Introduction:
The story of the universe, its birth, and its evolution is one of the most captivating narratives that science has to offer. At the heart of this cosmic epic lies the Big Bang Theory, a scientific framework that provides a compelling explanation for how our vast universe came into existence. In this blog, we’ll embark on a journey through time and space to explore the origins of the universe as described by the Big Bang Theory.
Chapter 1: In the Beginning
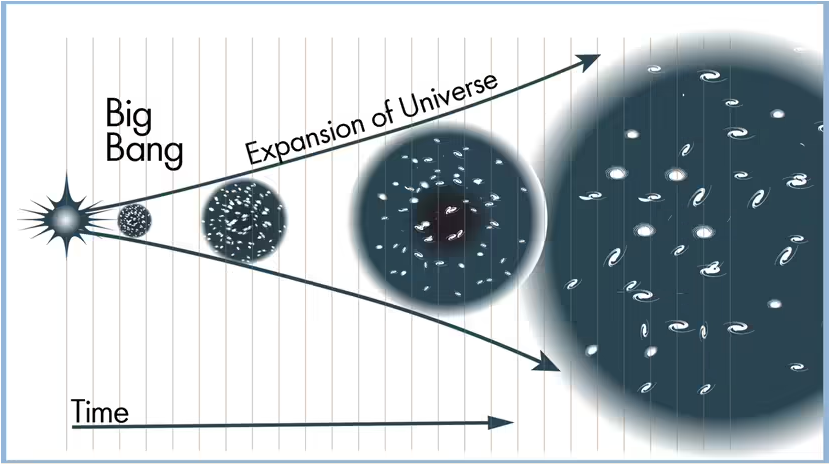
The Big Bang Theory posits that the universe was born from an unimaginably hot and dense singularity nearly 13.8 billion years ago. This singularity, a point where the known laws of physics break down, marked the inception of everything we see today. But how did we arrive at this theory?
- Early Clues: Scientists gathered early clues in the early 20th century when they observed that galaxies were moving away from each other. The universe was expanding, they realized, and this led to the idea of a cosmic beginning.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): A key piece of evidence supporting the Big Bang Theory is the discovery of the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). This faint glow of microwave radiation, originating from around 380,000 years after the Big Bang, provides a snapshot of the universe’s infancy.
Chapter 2: The Expanding Universe
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Big Bang Theory is the concept of cosmic expansion. Imagine rewinding the cosmic clock: as we move backward in time, the universe becomes denser and hotter. This expansion continues to this day, with galaxies receding from each other.
- Evidence for Expansion: The redshift of light from distant galaxies, observed by astronomers like Edwin Hubble, provides compelling evidence for cosmic expansion. The greater the distance to a galaxy, the greater its redshift, indicating that it’s moving away from us.
Chapter 3: The Birth of Matter and Stars
As the universe expanded and cooled, matter began to form. Primarily, hydrogen and helium atoms emerged from the cosmic soup. These atoms eventually coalesced into stars and galaxies.
- Star Formation: Inside the first generations of stars, nuclear fusion created heavier elements. This process seeded the universe with elements like carbon, oxygen, and iron, which are essential for the formation of planets, life, and everything we see around us.
Chapter 4: Galaxies and Cosmic Structure
Over billions of years, gravity brought galaxies together, forming the grand tapestry of the universe. Galaxies come in various shapes and sizes, from spirals to ellipticals, each with its own story to tell.
- Clusters and Superclusters: Galaxies didn’t stop at forming just on their own. They congregated into clusters and superclusters, creating the large-scale structure of the universe.
Chapter 5: Dark Mysteries
The Big Bang Theory also introduces us to two enigmatic cosmic components: dark matter and dark energy. While they remain mysterious, they play crucial roles in the universe’s evolution.
- Dark Matter: Dark matter provides the gravitational glue holding galaxies together. It’s invisible and doesn’t interact with light, making it challenging to detect directly.
- Dark Energy: Dark energy, on the other hand, is responsible for the universe’s accelerating expansion, a phenomenon discovered in the late 20th century.
Conclusion:
The Big Bang Theory is a powerful scientific framework that unravels the origins of our universe. From a hot and dense singularity to the cosmic microwave background radiation and the formation of galaxies, it offers a compelling narrative for the evolution of our universe over billions of years. Yet, it also leaves us with profound mysteries, such as the nature of dark matter and dark energy, waiting to be explored by future generations of scientists. The story of our universe is still being written, and it continues to inspire awe and wonder in all who seek to understand it.